
Swagelok® 밀폐제
Swagelok® 파이프 나사 밀폐제는 다양한 애플리케이션에서 누설 없는 밀폐를 보장함으로써 시스템 안전성을 강화합니다. Swagelok® TP 시리즈 열교환기 튜브 플러그는 열교환기의 수명을 연장하고 유지보수 비용을 절감할 수 있는 제품입니다.
밀폐제 보기Swagelok 파이프 나사 밀폐제는 다양한 화학물질과 호환성이 필요한 여러 애플리케이션에서 누설 없는 밀폐 성능을 제공합니다. 또한, 다양한 시스템 압력과 온도에 대응하는 등급입니다.
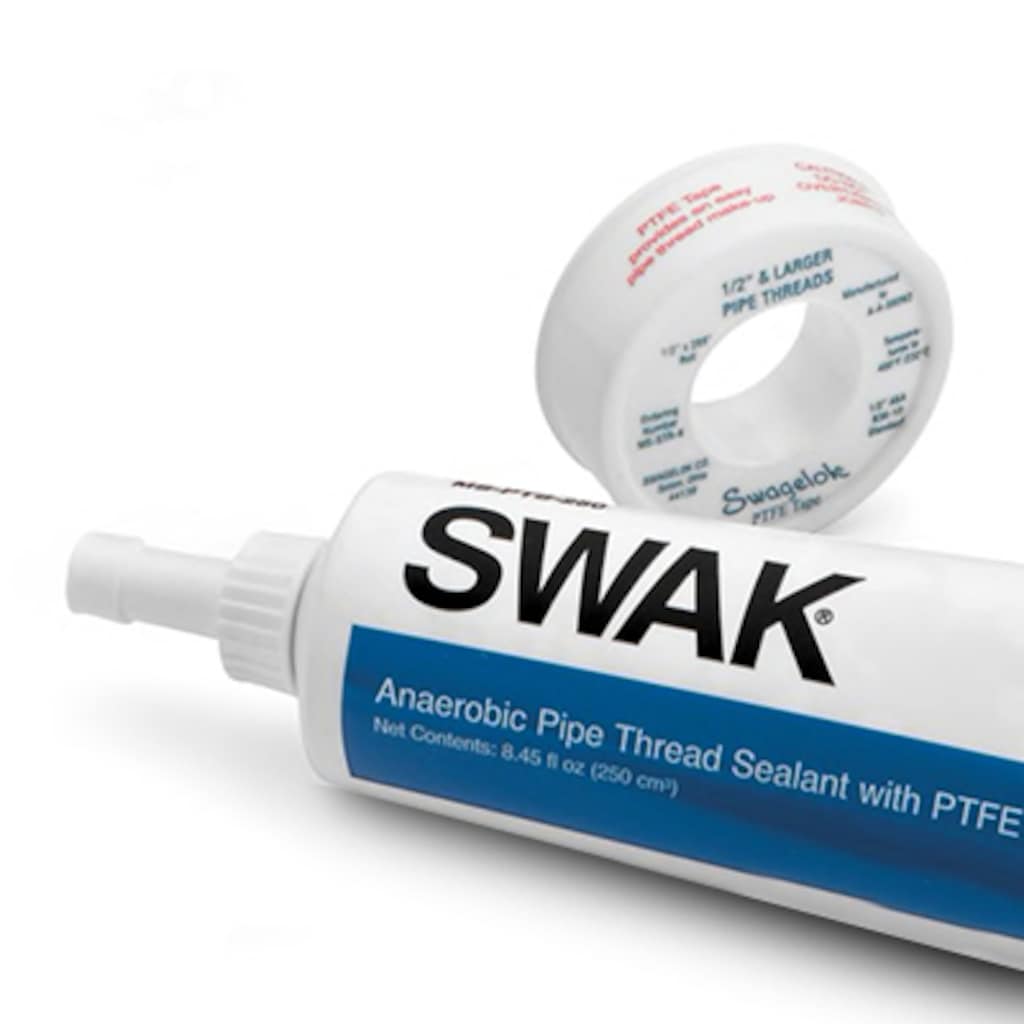
- Swagelok SWAK™ 혐기성 파이프 나사 밀폐제는 빠르고 손쉽게 도포할 수 있으며, 조립 중 파쇄되거나 찢어짐 없이 나사에 점착됩니다. 이 제품은 나사를 윤활하여 조립 중 마모와 협착으로 인한 많은 비용을 초래할 수 있는 나사 손상을 방지합니다. SWAK는 또한 진동 또는 충격에 대한 내성이 있는 본드로 경화되며, 낮은 이탈 토크(breakaway torque)로 완전히 경화된 후에도 손쉽게 풀 수 있는 연결구를 제공합니다.
- Swagelok® PTFE 없는 나사 밀폐제는 SWAK와 유사하게 작동하며, PTFE 기반 밀폐제가 바람직하지 않은 애플리케이션에서 즉각적인 밀폐 기능을 제공합니다.
- Swagelok® PTFE 테이프 파이프 나사 밀폐제는 미국 상용 제품 기술서 A-A-58092 규격을 준수하며, 최고 232°C(450°F)의 온도에서 수나사 경사나사 파이프 나사에 사용할 수 있습니다.
Swagelok® TP 시리즈 열교환기 튜브 플러그로 누설이 있는 튜브 끝을 밀폐하여 열교환기의 수명을 연장할 수 있습니다. 또한, 균일한 경사도와 매끄러운 표면처리로 설치할 때 최소한의 힘으로 양압 밀폐가 가능합니다. 튜브 플러그는 시스템 호환성을 보장할 수 있도록 다양한 재질로 공급 가능합니다.
나사 밀폐제에 대한 질문이 있으십니까?
Dichtmittel—Kategorien
Gewindedichtmittel
Die Gewindeschmiermittel sind mit vielen Chemikalien kompatibel und bieten in zahlreichen Anwendungen eine leckagefreie Abdichtung.
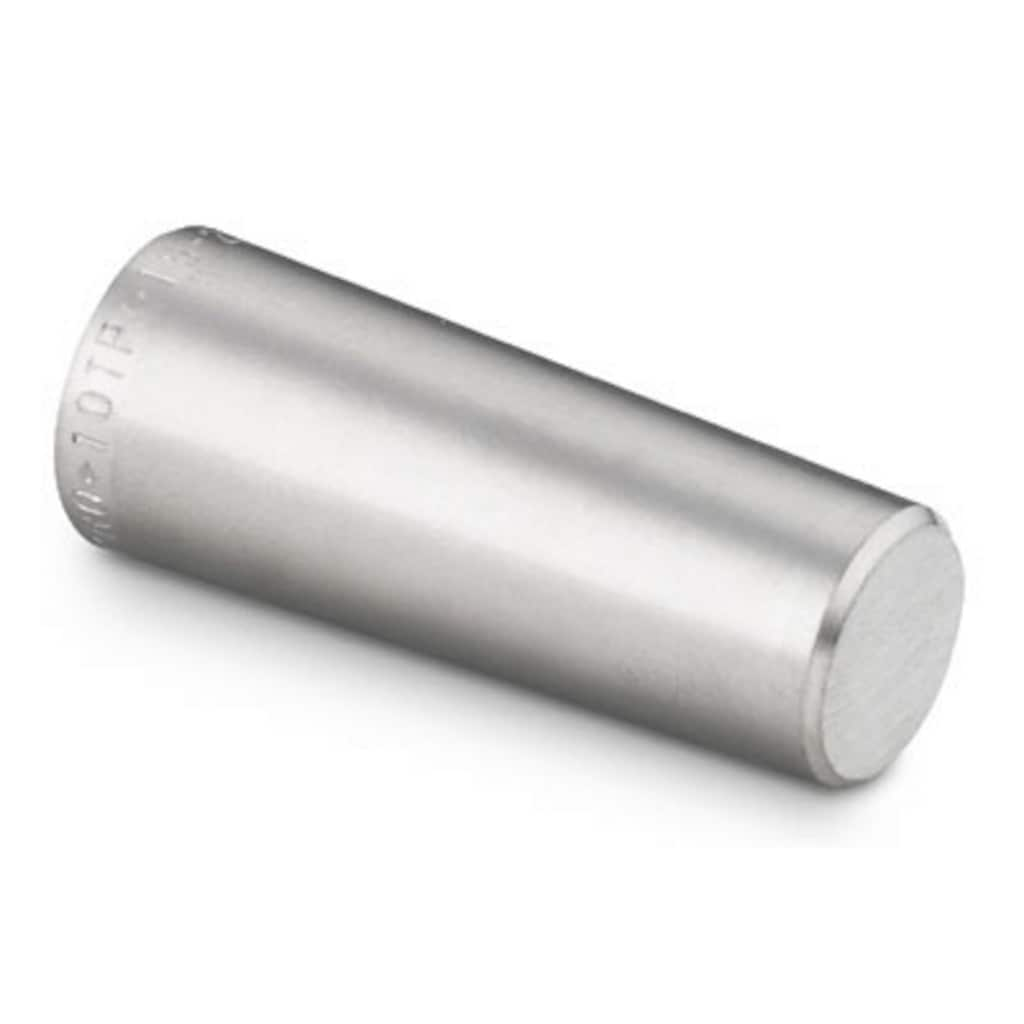

Rohrverschlussstopfen
Verschlussstopfen für Wärmetaucher zum Abdichten undichter Rohre – für eine längere Lebensdauer des Wärmetauschers.
밀폐제 카탈로그
구성 재질, 압력 및 온도 등급, 옵션, 액세서리를 포함한 자세한 제품 정보를 찾을 수 있습니다.
Produkte: Snoop® Lecksuchflüssigkeiten; Goop™ Gewindeschmiermittel ; SWAK®, PTFE-Gewindedichtband und PTFE-freie Gewindedichtmittel
Seiten 1-1. Merkmale: Stopfen für Wärmetauscherrohre dichten die Enden von undichten Rohren und verlängern so den Einsatz von Wärmetauschern.

압축 가스 누설 감지 서비스
압축 가스 누설을 식별하고 정량화하는 데 도움을 받음으로써, 누출 감소 가능성과 안전, 비용, 생산성 향상을 기준으로 해결해야 할 가장 중요한 문제의 우선순위를 정할 수 있습니다.
누설 감지 서비스에 대해 알아보기고객별 맞춤 선별 Swagelok 리소스

누설 감지 사례 연구
심층적인 기술과 애플리케이션 전문 지식을 갖춘 Swagelok 유체 시스템 전문가가 고객이 유체 시스템에서 누설을 찾고 대응하며 방지할 수 있도록 정기적으로 지원합니다. 고객에게 어떤 이점이 제공되었는지 알아보기

Распространенные причины и стоимость утечек в жидкостных и газовых системах
Самая незначительная утечка может стать причиной серьезной проблемы, когда перед вами стоят задачи обеспечения безопасности и рентабельности работы предприятия. Разберитесь, как и почему возникают утечки, как их можно обнаружить и проверить, и, наконец, как разработать стратегию по устранению и сокращению количества утечек в масштабе всего производства.

Борьба с утечками в жидкостных и газовых системах шинных производств
Производители шин могут не обращать внимания на утечки в технологических трубопроводах, однако именно они представляют существенную угрозу безопасности и рентабельности производства. Узнайте, как выявить наиболее распространенные источники утечек на предприятии, и методах их устранения.

Как избежать утечек в системе: Важно подготовить трубки
Эффективность монтажа трубных фитингов зависит от многих факторов, но одним из самых главных является надлежащая подготовка перед монтажом. Узнайте, как избежать дорогостоящих и опасных утечек, исключив поврежденные или неправильно отрезанные трубки и заусенцы.
